Introduction
Blood pressure is a key indicator of your overall health, acting as a silent, powerful metric that guides us in maintaining cardiovascular health and preventing complications. Managing blood pressure effectively not only helps in avoiding severe health issues but can also be the gateway to understanding your body better.
What Is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure measures the force of blood pushing against the walls of your arteries as it’s pumped by your heart. Here are the key components:
• Systolic Pressure: The pressure when your heart beats.
• Diastolic Pressure: The pressure when your heart rests between beats.
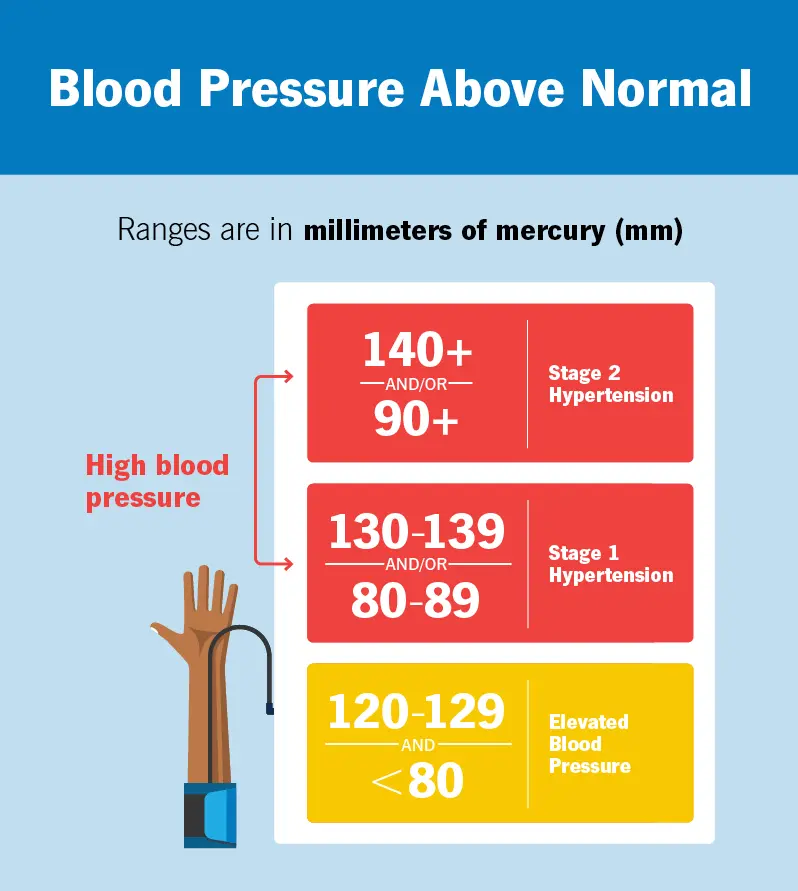
Healthy blood pressure is typically below 120/80 mmHg. Readings above this can range from elevated to hypertensive, requiring lifestyle adjustments or medical intervention.
What Is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure measures the force of blood pushing against the walls of your arteries as it’s pumped by your heart. Here are the key components:
• Systolic Pressure: The pressure when your heart beats.
• Diastolic Pressure: The pressure when your heart rests between beats.
Healthy blood pressure is typically below 120/80 mmHg. Readings above this can range from elevated to hypertensive, requiring lifestyle adjustments or medical intervention.
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure
Several factors can influence your blood pressure, including:
• Diet: High salt intake and low potassium hurt blood pressure levels.
• Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps lower blood pressure.
• Stress: Chronic stress can cause long-term increases in blood pressure.
• Genetics: Family history can play a significant role in your risk.
Monitoring Your Blood Pressure at Home
Regular monitoring at home can make a significant difference in early detection and management of high blood pressure. For accurate and reliable monitoring, Microlife blood pressure monitors are a top choice. These devices are easy to use and give you data that can help track your health trends over time.
How to Use a Blood Pressure Monitor
• Sit quietly for five minutes before taking a measurement.
• Position the cuff correctly on a bare arm at heart level.
• Remain still and silent during the measurement.
• Take measurements at the same times each day.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Blood Pressure
• Dietary Adjustments: Incorporate heart-healthy foods into your diet.
• Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
• Stress Management: Engage in relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If your measurements are consistently high, consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide guidance and, if necessary, medication to manage high blood pressure.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing your blood pressure are critical steps in maintaining your health. Regular monitoring can help you make informed decisions about lifestyle changes and when to seek medical advice.